Ad
OSNOVI NEUROANATOMIJE
- 1. I predavanje: ANATOMIJA NS
- 3. Dijelovi CNS:KičmenamoždinaMoždanostabloproduženamoždina, moždani most (pons)Srednjimozak (mezencefalon - midbrain) Mali mozakMedjumozak (diencefalon)Velikimozak (telencefalon)
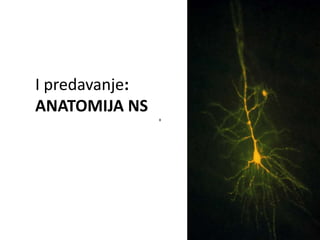
- 7. Potpornećelije - neuroglijaNeuronirazlicitoblik I velicinaDijelovi:TijeloDuginastavak – akson, možebitiodmotanmijelinili ne – mijeinizovan I nemijelinizovanKratkinastavak – dendrid
- 8. Mijelinizacijaaksona:- mijelin – izolatornervnogvlaknaMijelinizovaniilibijeliaksoni:- saltatornakondukacijaakcionihpotencijala – brziprenosuzmaliutrosakenergije
- 10. Neobicnioblicineurona – bogatorazgranjenjedendrita – dendriticnaarborizacija
- 13. 1. ProjekcioniA. ascendentni – aferentni - osjetnib. descendentni – eferentni - motorni2. asocijativni – povezujuudaljenedijelovemozga3. komisuralni - povezujulijevu I desnupolovinumozga
- 14. Asocijativniputevi: fasciculus longitudinalis superior i inferiorZULJEVITO TIJELO (corpus callosum) – komisuralni put – povezujedesnu I lijevuhemisferuvelikogmozga
- 15. Komisure: zuljevitotijelo, prednjakomisura, zadnjakomisura, komisurahipokampusa, komisurahabenula
- 16. Na ovojslici je prikazansljedeci putA. KomisuralniB. AsocijativniC: ProjekcioniMojodgovor je___
- 17. Tacanodgovor jeARadi se o zuljevitomtijelu
- 18. Na ovojslici je prikazansljedeci putA. KomisuralniB. AsocijativniC: ProjekcioniMojodgovor je__
- 19. Tacanodgovor jeBFasciculus arcuatus – lucni put kojipovezujerazlicitedijelovehemisferevelikogmozga s istestrane (okcipitalni – temporalni – parijetalni – frontalnilobus)
- 20. Komisuralnavlakna – zulevitotijelo I prednjakomisura
- 22. Nalazi se u kičmenomkanalu, odkoga je neštokračaObmotana je ovojnicama I opkoljena CS tečnošćuSadržibrojnaaferentna I eferentnavlaknakojapovezujumozaksaraznimdijelovimaorganizmaGradjenaizviševertikalnonaslaganihsegmenata
- 24. SPINALNI NERV-plavavlaknasuaferentna – osjetna- crvenavlaknasueferentna – somatska- crnavlaknasueferentna – autonomna
- 26. DERMATOMI
- 30. OrganizacijakicmenemozdineSiva masa: tijelaneurona I dendritiLokalizacijasinapseZadnjirog – zavrsavajuosjetnavlaknakicmenihzivacaPrednjirog – motornineuroni – polazistemotornihvlakanakicmenihzivacaLateralnirog – neuroni ANSBijelamasaPutevi: zadnja, prednja I bocnavrpca
- 34. Lumbalnapunkcija
- 35. 1. posterior horn 2. anterior horn 3. intermediate zone (intermediate gray) 4. lateral horn 5. posterior funiculus6. anterior funiculus7. lateral funiculus8. Lissauer's tract 9. anterior median fissure 10. posterior median sulcus 11. anterolateral sulcus 12. posterolateral sulcus 13. Posterior intermediate sulcus
- 37. Rexedovelamine
- 39. Neuronskikrugovikicmenemozdine – aferentnavlaknaizreceptora I njihovotokkrozkicmenumozdinu do prednjihrogiova, prikazanisulokalnineuroni - interneuroni
- 40. Kicmenamozdina I korijenovispinalnihnerava (prednji I zadnji)
- 41. PutevikicmenemozdineFasciculus GracilisFasciculus CuneatusTractus spinocerebellaris dorsalisTractus corticospinalis lateralisTractus spinothalamicus lateralisTractus spinocerebellaris ventralisTractus rubrospinalisTractus spinotectalisTractus corticospinalis anteriorTractus olivospinalisTractus spinoolivarisTractus tectospinalisTractus reticulospinalisTractus vestibulospinalisTractus spinothalamicus anteriorRaphe-spinal & Hypothalamospinal fibers16
- 43. MOZDANO STABLO
- 44. Basic Strucrure ofBrain Stem1. Tectum2. Tegmentum3. Basal Portion
- 45. Cranial NervesColumns ofBrain StemMotor Column1. GSE2. SVE3. GVESensory Column4. VA (GVA & SVA)5. GSA6. SSA
- 46. Reticular FormationA. Raphe NucleiB. Central Nuclear GroupC. Lateral Nuclear GroupD. Precerebellar Reticular NucleiABCD
- 47. Posterior White Column - medial Lemniscal Pathway& Spinothalamic Tract
- 48. Ascending Cortical System Special SensationBrain Stem Pathways for Special SensationGustatory Sensation (Taste, SVA) ----- Taste Pathway Auditory Sensation (Hearing, SSA) ----- Auditory PathwayVestibular Sensation (Equilibrium, SSA) ----- Vestibular Pathway
- 49. Auditory Pathway Modality: Auditory Sensation (Hearing) Receptor: Organ of Coti of Cochlear DuctCranial Nerve: VIIIc 1st Neuron: Spiral Ganglion 2nd Neuron: Cochlear Nucleus, Ventral & Dorsal dorsal, intermediate and ventral acoustic striae trapezoid body lateral lemniscus3rd Neuron: Inferior Colliculus brachium of inferior colliculus 4th Neuron: Medial Geniculate Nucleus (MG)auditory radiation Termination: Primary Auditory Area (A I)Brodmann area 31, 32
- 50. A. spiral ganglionB. dorsal and ventral cochlear nucleusC. inferior colliculusD. medial geniculate nucleusE. Primary auditory areaF. superior olivary nucleusG. nucleus of lateral lemniscus1. acoustic striae & trapezoid body2. lateral lemniscus3. brachium of inferior colliculus4. auditory radiation5. commissure of inferior colliculusVIIIc. cochlear divisionAuditory Pathways
- 51. Auditory PathwayA. spiral ganglionB. dorsal cochlear nucleusC. ventral cochlear nucleusD. superior olivary nucleus1. dorsal acoustic striae2. intermediateacoustic striae3. ventral acoustic striae4. efferent cochlear bundle5. trapezoid body6. lateral lemniscus
- 52. Vestibular Pathway Modality: Equilibrium Sensation Receptor: Macula & Crista Ampullaris Cranial Nerve: VIIIv Ist Neuron: Vestibular Ganglion 2nd Neuron: Vestibular Nucleus vestibulothalamic fiber (medial lemniscus)3rd Neuron: Thalamus (VPLo, VPI?) Internal Capsule ----- Corona Radiata Termination: Primary Vestibular Area----- Primary Somesthetic Area (Brodmann area 3a, 2v )
- 53. Vestibular Pathway 1. Vestibulocerebellar Tract2. Vestibulospinal Tract3. Vestibulothalamic Tract4. Medial Longitudinal fasciculus (MLF)- ascending portion - descending portion - interstitiospinal tract
- 54. Taste (Gustatory) Pathway Modality: Taste Sensation Receptor: Taste BudCranial Nerve: VII, IX, X Ist Neuron: Geniculate Ganglion (VII)Inferior Ganglion (IX, X) 2nd Neuron: Nucleus Tractus Solitarius(Gustatory Nucleus)solitariothalamic fiber (central tegmental tract)3rd Neuron: Thalamus (VPMpc) Internal Capsule ----- Corona Radiata Termination: Gustatory Area Brodmann area 43 & parainsular cortex
- 55. Composite BundleMedial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF)Dorsal Longitudinal Fasciculus (DLF)Central Tegmental Tract
- 56. Components of Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF) Descending ComponentsMedial Vestibulospinal Tract from medial and inferior vestibular nucleusInterstitiospinal Tract from interstitial nucleus of Cajal Ascending ComponentsEfferents from Medial Vestibular Nucleus contralateral III, IV, interstitial nucleus bilateral VI nucleusEfferents from Superior Vestibular Nucleus ipsilateral III, IV, interstitial nucleus
- 57. Components of Dorsal Longitudinal Fasciculus (DLF, fasciculus of Schütz) Ascending Componentssolitariohypothalamic fiber (visceral afferent fiber)ascending serotonergic fiber Descending Component descending fibers from hypothalamus to periaqueductal gray and dorsal tegmental nucleus
- 58. Mozdanostablo
- 59. MOZDANO STABLOJedrakranijalnihnerava – njihovapolazistailizavrseci
- 63. Produzeamozdina – regulacijakrvnogpritiska, povracanje
- 66. Kontrolabudnosti, spavanja, bola, tonusamisica, posturalnosti
- 70. Figure 9-9d: ANATOMY SUMMARY: The Brain
- 72. Periferninervnisistem – nerviPremapolozajuSpinalni (kicmeni) – 31 parKranijalni (mozdani) – 12 parAkoiduprema CNS – aferentninervi - osjetniAkoiduiz CNS – eferentninervi - motorniPremacilju u komezavršavaju – eferentninervi
- 73. Vegetativniiliautonomni – inervišužljezde I glatkemišiće
- 75. Cranial NervesTable 9-1: The Cranial Nerves
- 78. talamusKontrolorulaza u velikimozakSvaaferentnavlaknakojaidu ka velikommozguprolazekroztalamusSadržibrojnajedra
- 82. DiencephalonHomeostatic control centersThalamus – relay & sensory integrationHypothalamusHunger, stressThirst: body osmolarityFlight/fight pathwaysAnger & fearCircadian rhythmsCoordinate with endocrine
- 83. Pituitary and Pineal glandsPituitary trophic & other hormonesPineal MelatoninSleep coordinationFigure 9-10: The diencephalon
- 84. Classification of Thalamic Nuclei I. Lateral Nuclear Group II. Medial Nuclear Group III. Anterior Nuclear Group IV. Posterior Nuclear Group V. Metathalamic Nuclear Group VI. Intralaminar Nuclear Group VII. Thalamic Reticular Nucleus
- 86. Kora – starai novaSubkortikalnestrukture – nprbazalneganglije
- 87. Dijelovimozga
- 99. Pristupi analizi funkcionalne organizacije korteksa: PO FUNKCIONALNIM ODLIKAMA REGIONA
- 100. PREMA FUNKCIONALNIM SPECIFIČNOSTIMA ODREDJENIH OBLASTI: motorne senzorne asocijativne limbičke PREMA KARAKTERISTIKAMA CITOARHITEKTONSKIH POLJA(ORGANIZACIJA DESNE U ODNOSU NA LEVU HEMISFERU)
- 101. Principi organizacije (projekcija/veza): TOPOGRAFSKE MAPE
- 102. RAZDVOJENE I PARALELNE PROJEKCIJE
- 103. RECIPROČNE VEZE
- 104. ORGANIZACIJA ĆELIJA U SLOJEVE/LAMINE
- 105. KOLUMNEOrganizacija ćelija u lamine/slojeveUlaz(input)Izlaz(output)
- 106. Povezivanje susednih ćelija u kolumneUlaz(input)Izlaz(output)KOLUMNA
- 110. 3 MOZGA U JEDNOM
- 111. Veliki mozak (Telencephalon)Dvije hemisfereRazdvaja ih interhemisferična pukotina Spaja ih žuljevito telo (Corpus callosum) Spolja moždana kora (siva masa)Iznutra:Bela masa (ushodni i nishodni putevi)Limbički sistem i bazalne ganglije (sukortikalne sive mase)
- 112. Dubokajedra – bazalneganglijeLimbickisistemCingulatnigirus – emocijeHipokampus – ucenje I pamcenjeAmigdale – emocije I pamcenjeFigure 9-13: The limbic system
- 113. Figure 9-15: Functional areas of the cerebral cortex Koravelikogmozga: debljina 1 mm
- 114. Režnjevi velikog mozgaLinije razdvajanja:Centralna Rolandova brazda (Sulcus centralis Rolandi)Lateralna Silvijeva jama (Fissura cerebri lateralis Sylvii)FrontalniParijetalni TemporalniOkcipitalni Limbički režanj
- 116. Cingulate gyrusAnterior nucleus of thalamusThalamusPara-olfactoryareaFornixMamillary bodies ofhypothalamusHypothalamusHippocampusUncusAmygdalaPara-hippocampalgyrus
- 117. Režnjevi velikog mozga (lobusi)Frontalni (čeoni):
- 120. Prefrontalni regioni
- 126. Auditivna asocijativna kora
- 129. Vizuelna asocijativna koraLIMBIČKI SISTEM (režanj)
- 130. Motor cortexSomatosensory cortexSensory associativecortexParsopercularisVisual associativecortexBroca’sareaVisualcortexPrimaryAuditory cortexWernicke’sarea
- 133. KLASIČNA FUNKCIONALNA PODELA KORE MOZGAMOTORNE OBLASTIPRECENTRALNA/MOTORNA KORA PREMOTORNA KORA BROKAOVA ZONA (FRONT.OPERKULUM) FRONTALNA OČNA POLJASENZORNE OBLASTIVIDNA/VIZUELNA KORA/AREA STRIATA, SLUŠNA/AUDITIVNA KORA, SOMATOSENZORNA/POSTCENTRALNA KORA i oblasti koje ih okružuju (BA 18 i 19; srednja parijetalna kora; temporalna ravan)3. ASOCIJATIVNE OBLASTIpreostali neokorteks4. LIMBIČKE OBLASTI parahipokampalna kora (T) entorinalna kora (F) cingularni pojas
- 134. BA 1,2,3BA 4Primarne senzornei motorne oblastiBA 41,42BA 17N.B. Asocijativne oblasti-sivo obojene; limbičke-locirane više medijalno, skrivene u lateralnom pogledu na hemisferu
- 138. Primary motor cortex (M1)Posterior parietal cortexSupplementarymotor cortex(SMA)Premotor cortex(PMA)
- 139. Motor cortexSomatosensory cortexSensory associativecortexParsopercularisVisual associativecortexBroca’sareaVisualcortexPrimaryAuditory cortexWernicke’sarea
- 140. Funkcije kore mozgaPrijem, obrada i skladištenje informacija (II funkcionalni blok – Luria),Programiranje, regulisanje i kontrola motornih i složenih psihičkih aktivnosti (III funkcionalni blok – Luria)
- 141. Funkcije kore mozga -1.Prijem i obrada informacija (II funkc. Blok-Luria):Parijetalni (temeni):Primarna somatosenzorna koraSomatosenzorna asocijativna kora:Unimodalna (modalno specifična ) obrada taktilnih informacijaHeteromodalna ( modalno nespecifična) obrada informacija Temporalni (slepoočni):Primarna auditivna koraAuditivna asocijativna kora:Unimodalna (modalno specifična ) obrada slušnih informacijaHeteromodalna (modalno nespecifična) obrada informacija Okcipitalni (zatiljačni):Primarna vizuelna koraVizuelna asocijativna kora:Unimodalna (modalno specifična ) obrada vidnih informacijaHeteromodalna (modalno nespecifična) obrada informacija
- 142. Funkcije kore velikog mozga – 2. Programiranje, regulisanje i kontrola motornih i složenih psihičkih aktivnosti (III funkcionalni blok – Luria):Frontalni (čeoni) režanj:Primarna motorna kora (Area 4 Brodmann)Sekundarna motorna kora (premotorna; area 6)Frontalna area pogleda- okulomotorna kora (area 8)Motorno govorno polje – Broca (area 44) Prefrontalni regioni (Frontalni asocijacioni regioni)
- 143. Frontalni (čeoni) režanjPrimarna motorna kora (area 4)Premotorna kora (area 6)Frontalna area pogleda (area 8)Motorno govorno polje - Broca( area 44)Frontalna asocijaciona polja (Prefrontalna kora)
- 144. Parijetalni (temeni) režanjPrimarna senzitivna kora (postcentralna vijuga: area 3, 2, 1)Sekundarna senzitivna kora (area 5 i 7)Asocijativna kora (area 39 i 40)Gyrus angularisGyrus supramarginalis
- 145. Temporalni (slepoočni) režanjTemporalni neokorteks (lateralna strana T.R.) : Primarna auditivna kora (area 41,)Sekundarna auditivna kora (area 42)Asocijaciona kora: T-P-O raskršće (area 38 ,20, 21, i 22 )Limbički sistem – deo (medijalna strana TR) :Gyrus parahippocampalis
- 146. Okcipitalni (zatiljačni) režanjPrimarna vidna kora(area 17 ili tzv. area striata): Završetak vidnog puta (radiatio optica Gratioleti):Vlakna iz dve desne polovine retine (leve polovine vidnog polja) završavaju u desnom okcipitalnom režnju, Vlakna iz dve leve polovine retine (desne polovine vidnog polja) završavaju u levom okcipitalom režnju. Sekundarna vidna kora(area 18 ili tzv. area parastriata)Asocijativna vidna kora (area 19 ili tzv. area peristriata)
- 158. Brodman’s Map of Motor and Sensory Areas
- 160. Isocortex – typical 6 layered cortex I. Molecular LayerII. External Granular LayerIII. External Pyramidal LayerLine of Kaes-BechterewIV. Internal Granular LayerOuter band of Baillarger - Line of Gennari in area 17 V. Internal Pyramidal LayerGiant pyramidal cell of BetzInner Band of BaillargerVI. Polymorphic LayerGolgi NisslWeigert
- 161. 5 PREDAVANJE SISTEM MOZDANIH KOMORA I CEREBROSPINALNI LIKVOR
- 167. Cerebrospinal FluidFrom coracoid plexusFills ventricles & subarachnoidFluid pillow floats brainExchange transport From bloodTo brain tissue
- 168. Cerebrospinal FluidFigure 9-5: ANATOMY SUMMARY: Cerebrospinal Fluid
- 176. Blood Brain BarrierExtensive capillaries & sinusesTight junctions: limit permeabilityAstrocyte foot processes: secrete paracrinesProtects brain: hormones & circulating chemicalsMany glucose transportersFigure 9-6: The blood-brain barrier